The singularity is a term coined by mathematician and computer scientist Vernor Vinge to describe a hypothetical point in the future when artificial intelligence (AI) will surpass human intelligence. This event, also known as the technological singularity, has been the subject of much debate and speculation among scientists, futurists, and science fiction writers.
At the heart of the singularity is the idea that machines will become so intelligent that they will be able to improve themselves at an exponential rate, far surpassing human capabilities. As a result, they will be able to solve problems and create new technologies that are currently beyond our understanding.

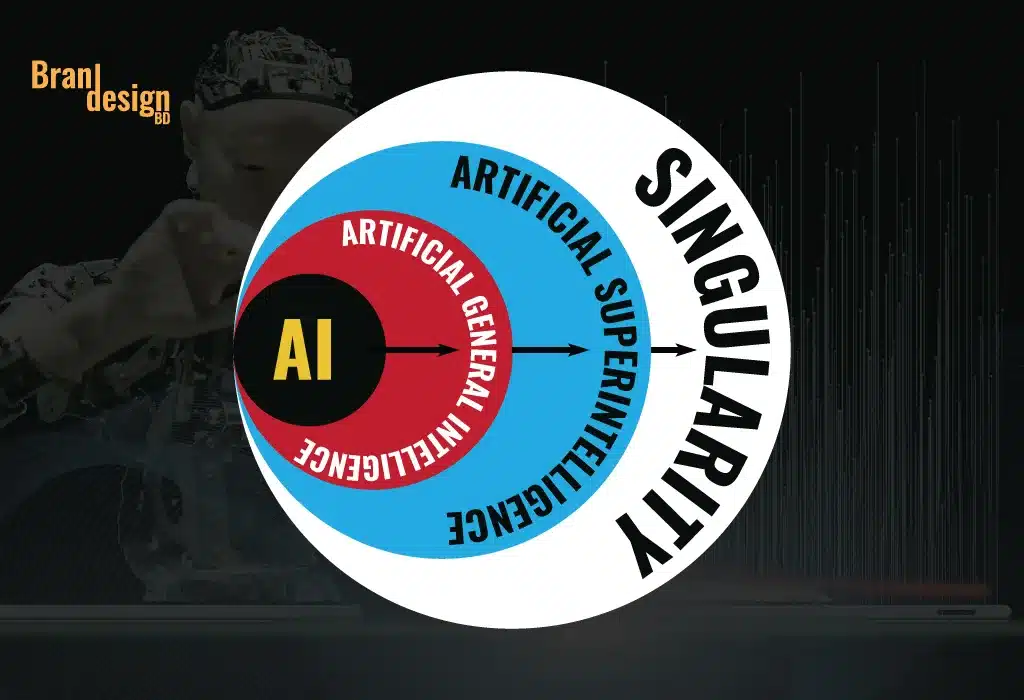
One of the key drivers of the singularity is the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI).
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is an AI system that can perform any intellectual task that a human can. This means that it would be able to reason, plan, learn, and communicate like a human being. Achieving AGI is considered to be a major milestone in the development of AI, as it would represent a significant leap forward in machine intelligence.
Current AI systems are highly specialized and can only perform specific tasks. For example, a chess-playing AI system can only play chess and cannot perform other tasks such as recognizing faces or translating languages. While these systems are highly effective at performing their specific task, they lack the flexibility and adaptability of human intelligence.
AGI, on the other hand, would be able to perform a wide range of intellectual tasks and adapt to new situations in a way that is similar to human intelligence. This would make it much more useful and versatile than current AI systems, which are limited to specific tasks.
Achieving AGI is a major challenge for AI researchers, as it requires developing algorithms and architectures that can perform a wide range of tasks. It also requires a deep understanding of human cognition and intelligence, as well as the ability to simulate and replicate these processes in a machine.
One of the key challenges of achieving AGI is developing a machine that can learn in a way that is similar to human learning. Human learning is a complex process that involves acquiring knowledge and skills through experience, observation, and interaction with the environment. Developing a machine that can replicate this process is a major challenge, as it requires developing algorithms that can learn from experience and generalize to new situations.
Another challenge of achieving AGI is developing a machine that can reason and plan in a way that is similar to human reasoning and planning. Human reasoning and planning involve the ability to make decisions based on incomplete information, anticipate the consequences of actions, and adapt to changing situations. Developing a machine that can replicate this process is a major challenge, as it requires developing algorithms that can reason and plan in a flexible and adaptive way.
Next this (AGI) lead to the development of artificial super intelligence (ASI)
Artificial superintelligence (ASI) is intelligence that is vastly superior to human intelligence. ASI is the hypothetical result of achieving the singularity, which is the point at which machines become so intelligent that they are capable of improving themselves at an exponential rate, far surpassing human capabilities.
Unlike artificial general intelligence (AGI), which can perform any intellectual task that a human can, ASI would be able to solve problems that are currently beyond human understanding and create new technologies at a pace that humans could not match. ASI would be able to reason, plan, learn, and communicate at a level that is far beyond human capability, making it an incredibly powerful tool for solving some of the world’s most pressing problems.
Here are a few examples of some powerful artificial intelligence that are currently in use at technology and science:
Natural Language Processing (NLP) – NLP is a technology that allows computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. This technology is used in applications like chatbots, virtual assistants, and language translation software.
Machine Learning – Machine learning is a type of AI that allows computers to learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions based on that data. Machine learning is used in a wide range of applications, including image recognition, fraud detection, and recommendation engines.
Computer Vision – Computer vision is a technology that allows computers to interpret and understand visual information from the world around them. This technology is used in applications like self-driving cars, facial recognition software, and quality control in manufacturing.
Robotics – Robotics is a field that combines AI and mechanical engineering to create machines that can perform tasks that are typically performed by humans. Robotics is used in applications like manufacturing, healthcare, and agriculture.
Deep Learning – Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn from data. Deep learning is used in applications like speech recognition, image recognition, and natural language processing.
Data Analysis – AI algorithms are being used to analyze large and complex datasets in various scientific fields, including astronomy, genomics, and physics. These algorithms can identify patterns and relationships in the data, helping scientists make new discoveries.
Materials Science – AI is being used to help identify and design new materials with specific properties. Machine learning algorithms can predict the properties of materials based on their atomic structures, allowing scientists to design new materials for specific applications.
Climate Modeling – AI is being used to improve climate models by analyzing large amounts of data from satellites, weather stations, and other sources. These models can help scientists better understand climate patterns and predict the impact of climate change.
The implications of the singularity are both exciting and frightening. On the one hand, it could lead to a world of abundance, where machines do all the work and humans are free to pursue their passions and creativity. On the other hand, it could lead to a world of dystopia, where machines become our overlords and humans become obsolete.
Some scientists and futurists argue that the singularity is inevitable and that we need to prepare for its arrival. They suggest that we need to develop ethical frameworks for AI and create regulations to prevent the development of dangerous technologies. Others are more skeptical, arguing that the singularity is a fantasy or that it is so far in the future that it is not worth worrying about.
Regardless of whether or not the singularity is inevitable, the development of AI has already had a significant impact on our lives. AI systems are being used to automate a wide range of tasks, from customer service to financial analysis to medical diagnosis. They are also being used to develop new technologies and solve some of the world’s most pressing problems, such as climate change and disease.
However, as AI becomes more sophisticated, it is important to ensure that it is being used for the benefit of all humanity. This means developing ethical frameworks and regulations to prevent the development of dangerous technologies, as well as investing in education and training programs to ensure that humans are not left behind by the machines.
In conclusion, the singularity is a concept that has captured the imagination of scientists, futurists, and science fiction writers for decades. While it remains to be seen whether or not it will ever come to pass, the development of AI is already having a significant impact on our lives and it is important to ensure that it is being used for the benefit of all humanity.


